end tidal co2 range dog
Leaking anesthetic circuit. This is end-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 which is normally 35 to 45 mm Hg in dogs and 28 to 32 mm Hg in cats.

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall
The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.

. Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. Love and Harvey 2006.
Variants of normal ETCO2 tracings from normal anesthetized animals. Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law. The end-tidal carbon dioxide will not necessarily reflect arterial carbon dioxide levels and the gradient between arterial and end-tidal carbon dioxide cannot.
59 Additional reasons for rapid decreases include. The measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 allows the continuous monitoring of the adequacy of ventilation and circulation in the anaesthetised patientIt measures inspired and expired carbon dioxide CO 2 throughout the whole respiratory cycle using infrared spectroscopyETCO 2 can be of value in the assessment of ventilation metabolism and of a. According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg.
1 End-tidal CO2 usually underestimates PaCO 2 by 2-5 mm Hg in mammals. This trace is considered to be normal 2. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector.
The 1 inhaled CO2 produced a significant. Normal range is 35-45mmHg and roughly correlates with the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood remember that PaCO2 is usually slightly higher than ETCO2 by 2-5mmHg. Common narrow plateaus seen during.
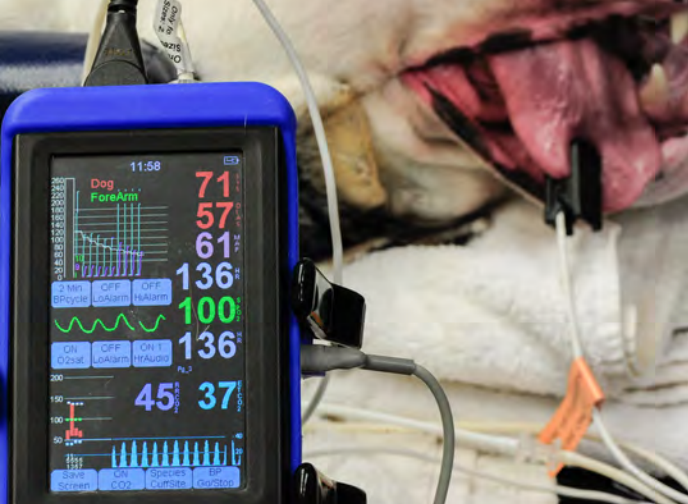
Capnography also measures and displays the respiratory rate. In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring.
Normal arterial blood pressure values for dogs and cats are indicated in Table 111. A total of eight experiments were performed in four dogs comprising 31 control observations and 23 CO2 inhalation observations. Thus ETCO 2 provides continuous noninvasive quantitation of adequacy of ventilation.
End-tidal CO2 as a guide to successful cardiopulmonary. End-tidal carbon dioxide levels correlate fairly well with arterial carbon dioxide PaCO 2. A total of eight experiments were performed in four dogs comprising 31 control observations and 23 CO2 inhalation observations.
The steady-state end-tidal CO2 tension PCO2 was examined during control and 1 CO2 inhalation periods in awake beagle dogs with an intact airway breathing through a low dead-space respiratory mask. The end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PetCO2 measured after a single large tidal-volume breath 15 mlkg body weight was compared to simultaneous measurements of PaCO2 in 6 dogs with normal lungs who were receiving high-frequency jet ventilation HFJV. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective.
End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 monitoring is recommended for intubated patients at risk of CPA I-A. This is end-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 which is normally 35 to 45 mm Hg in dogs and 28 to 32 mm Hg in cats. The steady-state end-tidal CO2 tension PCO2 was examined during control and 1 CO2 inhalation periods in awake beagle dogs with an intact airway breathing through a low dead-space respiratory mask.
The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle. However an excess of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream can lead to an abnormal condition causing symptoms ranging from dizziness to convulsions. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. Most anesthetics are respiratory depressants and end-tidal CO2 allows early detection of respiratory impairment so appropriate intervention can occur before the problem becomes life threatening.
25 EtCO2 correlates well with cardiac output and rapidly drops to zero at CPA onset. Values for hypercapnia range from 65-75 mm Hg. Assess the patients pulse and monitor end-tidal carbon dioxide production.
To determine whether the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide PetCO 2 could predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in patients with cardiopulmonary arrest CPA undergoing CPR. 48 When a person is breathing out CO 2 the graph goes up. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective.
2 See Figure 1 p. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. PaCO2 PetCO2 End tidal measurement from expired or exhaled air PaCO2 Arterial blood gas sample End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation.
The normal range for ETCO 2 in mammals is 35-45 mm Hg. There was an excellent linear correlation between PetCO2 and the PaCO2 over the entire range of CO2 tensions. Thirty-five client-owned dogs and cats in CPA in which CPR was performed.
Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns. Values above 40 - 45 mm Hg for ETCO. We know that elevated ETCO2 hypercapnia occurs during hypoventilation and a decrease in ETCO2 hypocapnia occurs with hyperventilation.
When a person is breathing in it. However because they are consistent over a wide range of pressures they are considered reliable Durham 2005. Examples of some common capnograms are.
2 See Figure 1 p. Left untreated a state of hypercapnia can lead to death. Two private specialty referral hospitals.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. The capnograph is the waveform that shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle and it normally has a rectangular shape Figure 1. The normal amount of carbon dixide in the arterial blood is 35-45 mm Hg a measurable unit of pressure.
With a normal range of 35 - 45 mm Hg.
Capnography In Veterinary Medicine Chapter 28 Capnography
The Abcs Of Veterinary Dentistry V Is For Ventilation Monitoring

Pet Emergency Poster Pet Emergency Pet Clinic Veterinarian Education

We Make 3d Selfie 3d Figurine Made Of Sandstone Just From Your Photo Pets Family Figurine Figurines

Pet Anesthesia And Patient Monitoring Westbridge Veterinary Hospital

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Veterinary Use Contec Ca10m Vet With 2 Gas Adapters Mainstream Etco2 C

The Practitioner S Acid Base Primer Obtaining Interpreting Blood Gases Today S Veterinary Practice

The Beatles Dog Collar Size Xs S M Or L Etsy Dog Collar Size Dog Collar Training Collar

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall
Did You Know Hypercapnia Is Synonymous With Hypoventilation

Small Animal Anesthesia Techniques Ebook By Carolyn M Mckune Rakuten Kobo In 2022 Small Pets Animals Veterinary

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

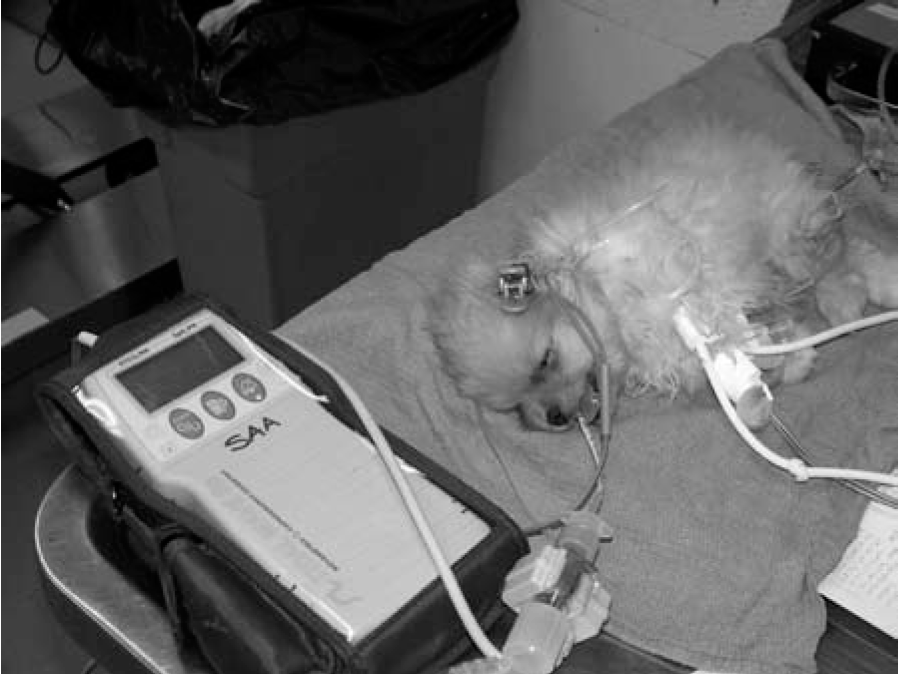
Concurrent Use Of Pulse Oximetry Via A Tongue Probe And Capnometry In An Anesthetized Dog Hemoglobin Satura Vet Tech School Vet Medicine Veterinary Medicine

The High Cost High Risk World Of Modern Pet Care Modern Pet Pets Pet Insurance Reviews

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

